大数据学习
bigdata learning
Toggle navigation
大数据学习
主页
openGauss数据库
Flume
MongoDB
Hadoop
数据库实验
Kafka
Zookeeper
Hbase
Manual
Spark
Neo4j
InfluxDB
RabbitMQ
Flink
About Me
归档
标签
02-Yarn配置
Hadoop
2022-12-10 21:16:27
321
0
0
bigdata
Hadoop
# Yarn基本配置 1. 修改mapred-site.xml 由于在配置文件目录`cd /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/`下没有,需要将`mapred-site.xml.template`复制为`mapred-site.xml` ```bash nbu@ecs:~$ cd /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/ nbu@ecs:/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop$ cp mapred-site.xml.template mapred-site.xml nbu@ecs:/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop$ vim mapred-site.xml ``` ```xml <configuration> <!-- 通知框架MR使用YARN --> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property> </configuration> ``` 2. 修改yarn-site.xml,修改内容如下 ```bash nbu@ecs:/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop$ vim yarn-site.xml ``` ```xml <configuration> <!-- reducer取数据的方式是mapreduce_shuffle --> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name> <value>localhost</value> </property> </configuration> ``` 3. 启动yarn ```bash nbu@ecs:~$ /usr/local/hadoop/sbin/start-yarn.sh # 执行MapReduce任务 pi nbu@ecs:~$ hadoop jar /usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.7.1.jar pi 10 10 ``` 在浏览器中输入localhost:8088查看 Applications--RUNNING中运行的任务 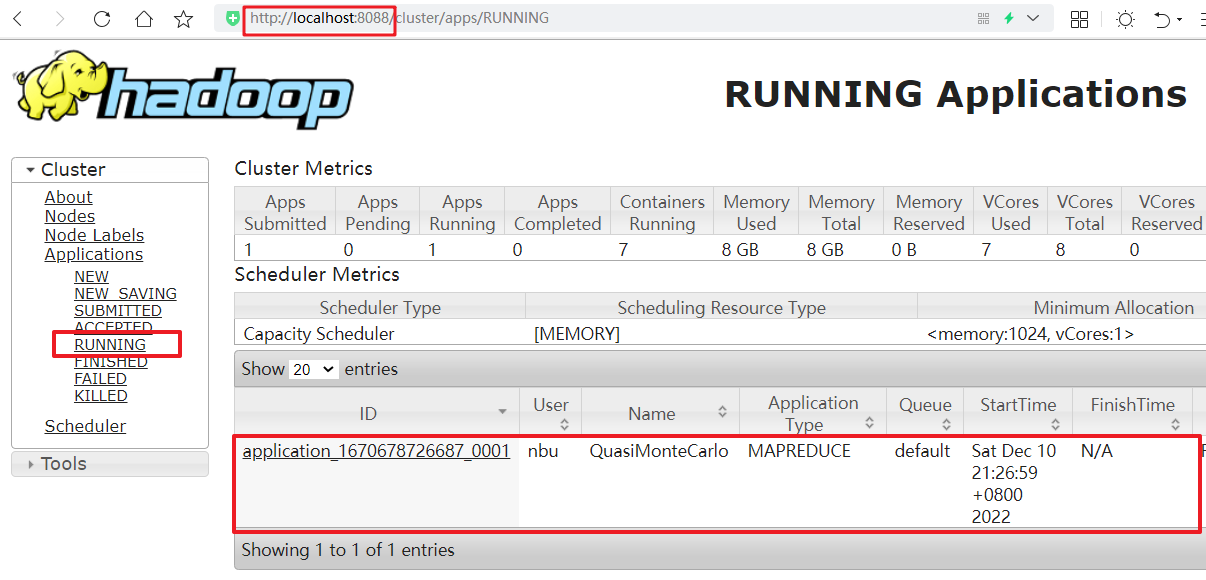 可以输入yarn命令来查看已经结束的任务 ```bash nbu@ecs:~$ yarn application -list -appStates FINISHED ``` 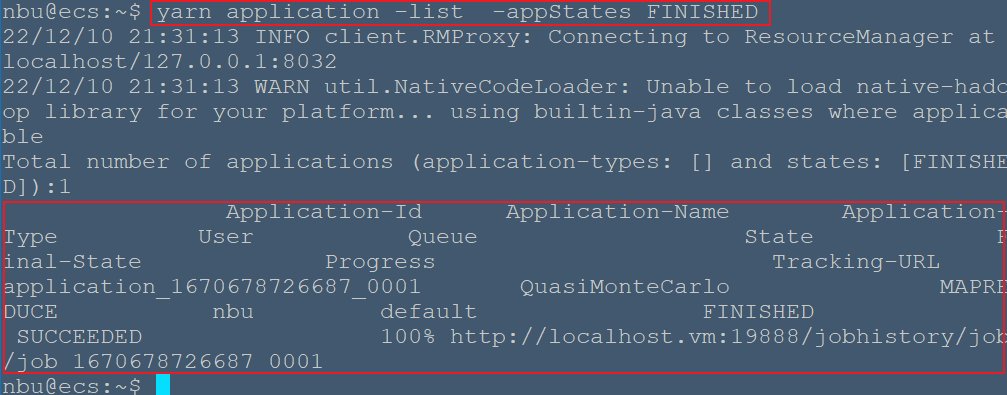 # 命令详解 1. application 2. applicationattempt 3. classpath 4. container 5. jar 6. logs 7. node 8. queue 9. daemonlog 10. nodemanager 11. proxyserver 12. resourcemanager 13. rmadmin 14. scmadmin 15. sharedcachemanager 16. timelineserver ## application 使用语法:yarn application [options] #打印报告,申请和杀死任务 ``` -appStates <States> #与-list一起使用,可根据输入的逗号分隔的应用程序状态列表来过滤应用程序。有效的应用程序状态可以是以下之一:ALL,NEW,NEW_SAVING,SUBMITTED,ACCEPTED,RUNNING,FINISHED,FAILED,KILLED -appTypes <Types> #与-list一起使用,可以根据输入的逗号分隔的应用程序类型列表来过滤应用程序。 -list #列出RM中的应用程序。支持使用-appTypes来根据应用程序类型过滤应用程序,并支持使用-appStates来根据应用程序状态过滤应用程序。 -kill <ApplicationId> #终止应用程序。 -status <ApplicationId> #打印应用程序的状态。 ``` ## applicationattempt 使用语法:yarn applicationattempt [options] #打印应用程序尝试的报告 ``` -help #帮助 -list <ApplicationId> #获取到应用程序尝试的列表,其返回值ApplicationAttempt-Id 等于 <Application Attempt Id> -status <Application Attempt Id> #打印应用程序尝试的状态。 ``` ## classpath 使用语法:yarn classpath #打印需要得到 Hadoop 的 jar 和所需要的 lib 包路径 ## container 使用语法:yarn container [options] #打印 container(s) 的报告 ``` -help #帮助 -list <Application Attempt Id> #应用程序尝试的Containers列表 -status <ContainerId> #打印Container的状态 ``` ## jar 使用语法:yarn jar <jar> [mainClass] args... #运行 jar 文件,用户可以将写好的 YARN 代码打包成 jar 文件,用这个命令去运行它。 ## logs 使用语法:yarn logs -applicationId <application ID> [options] #转存 container 的日志。 ``` -applicationId <application ID> #指定应用程序ID,应用程序的ID可以在yarn.resourcemanager.webapp.address配置的路径查看(即:ID) -appOwner <AppOwner> #应用的所有者(如果没有指定就是当前用户)应用程序的ID可以在yarn.resourcemanager.webapp.address配置的路径查看(即:User) -containerId <ContainerId> #Container Id -help #帮助 -nodeAddress <NodeAddress> #节点地址的格式:nodename:port (端口是配置文件中:yarn.nodemanager.webapp.address参数指定) ``` ## node 使用语法:yarn node [options] #打印节点报告 ``` -all #所有的节点,不管是什么状态的。 -list #列出所有RUNNING状态的节点。支持-states选项过滤指定的状态,节点的状态包含:NEW,RUNNING,UNHEALTHY,DECOMMISSIONED,LOST,REBOOTED。支持--all显示所有的节点。 -states <States> #和-list配合使用,用逗号分隔节点状态,只显示这些状态的节点信息。 -status <NodeId> #打印指定节点的状态。 ``` ## queue 使用语法:yarn queue [options] #打印队列信息 ``` -help #帮助 -status #<QueueName> 打印队列的状态 ``` ## daemonlog 使用语法: yarn daemonlog -getlevel <host:httpport> <classname> yarn daemonlog -setlevel <host:httpport> <classname> <level> ``` -getlevel <host:httpport> <classname> #打印运行在<host:port>的守护进程的日志级别。这个命令内部会连接http://<host:port>/logLevel?log=<name> -setlevel <host:httpport> <classname> <level> #设置运行在<host:port>的守护进程的日志级别。这个命令内部会连接http://<host:port>/logLevel?log=<name> ``` ## nodemanager 使用语法:yarn nodemanager #启动 nodemanager ## proxyserver 使用语法:yarn proxyserver #启动 web proxy server ## resourcemanager 使用语法:yarn resourcemanager [-format-state-store] #启动 ResourceManager ``` -format-state-store # RMStateStore的格式. 如果过去的应用程序不再需要,则清理RMStateStore, RMStateStore仅仅在ResourceManager没有运行的时候,才运行RMStateStore ``` ## rmadmin 使用语法: #运行 Resourcemanager 管理客户端 ``` yarn rmadmin [-refreshQueues] [-refreshNodes] [-refreshUserToGroupsMapping] [-refreshSuperUserGroupsConfiguration] [-refreshAdminAcls] [-refreshServiceAcl] [-getGroups [username]] [-transitionToActive [--forceactive] [--forcemanual] <serviceId>] [-transitionToStandby [--forcemanual] <serviceId>] [-failover [--forcefence] [--forceactive] <serviceId1> <serviceId2>] [-getServiceState <serviceId>] [-checkHealth <serviceId>] [-help [cmd]] ``` ``` -refreshQueues #重载队列的ACL,状态和调度器特定的属性,ResourceManager将重载mapred-queues配置文件 -refreshNodes #动态刷新dfs.hosts和dfs.hosts.exclude配置,无需重启NameNode。 #dfs.hosts:列出了允许连入NameNode的datanode清单(IP或者机器名) #dfs.hosts.exclude:列出了禁止连入NameNode的datanode清单(IP或者机器名) #重新读取hosts和exclude文件,更新允许连到Namenode的或那些需要退出或入编的Datanode的集合。 -refreshUserToGroupsMappings #刷新用户到组的映射。 -refreshSuperUserGroupsConfiguration #刷新用户组的配置 -refreshAdminAcls #刷新ResourceManager的ACL管理 -refreshServiceAcl #ResourceManager重载服务级别的授权文件。 -getGroups [username] #获取指定用户所属的组。 -transitionToActive [–forceactive] [–forcemanual] <serviceId> #尝试将目标服务转为 Active 状态。如果使用了–forceactive选项,不需要核对非Active节点。如果采用了自动故障转移,这个命令不能使用。虽然你可以重写–forcemanual选项,你需要谨慎。 -transitionToStandby [–forcemanual] <serviceId> #将服务转为 Standby 状态. 如果采用了自动故障转移,这个命令不能使用。虽然你可以重写–forcemanual选项,你需要谨慎。 -failover [–forceactive] <serviceId1> <serviceId2> #启动从serviceId1 到 serviceId2的故障转移。如果使用了-forceactive选项,即使服务没有准备,也会尝试故障转移到目标服务。如果采用了自动故障转移,这个命令不能使用。 -getServiceState <serviceId> #返回服务的状态。(注:ResourceManager不是HA的时候,时不能运行该命令的) -checkHealth <serviceId> #请求服务器执行健康检查,如果检查失败,RMAdmin将用一个非零标示退出。(注:ResourceManager不是HA的时候,时不能运行该命令的) -help [cmd] #显示指定命令的帮助,如果没有指定,则显示命令的帮助。 ``` ## scmadmin 使用语法:yarn scmadmin [options] #运行共享缓存管理客户端 ``` -help #查看帮助 -runCleanerTask #运行清理任务 ``` ## sharedcachemanager 使用语法:yarn sharedcachemanager #启动共享缓存管理器 ## timelineserver 使用语法:yarn timelineserver #启动 timelineserver
上一篇:
02-Spark-Shell命令
下一篇:
02-Zookeeper安装配置
文档导航